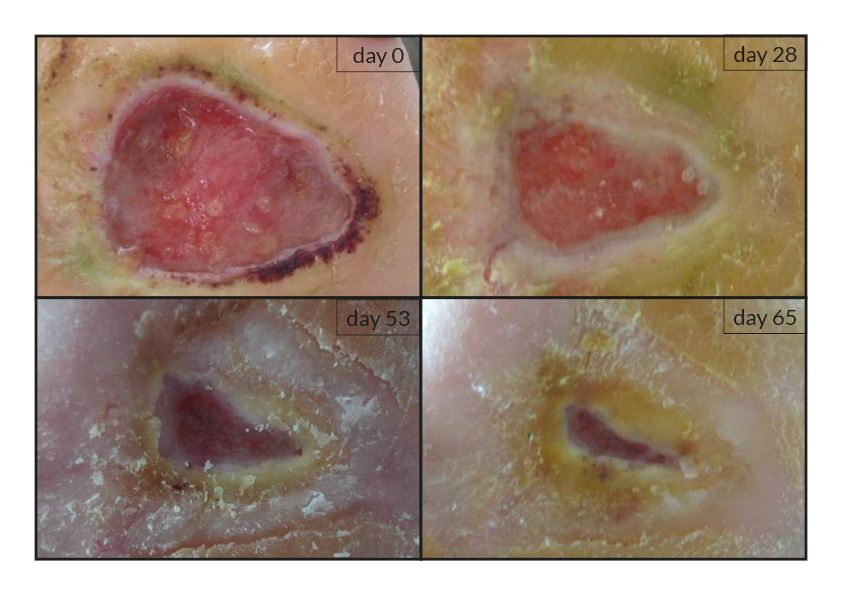
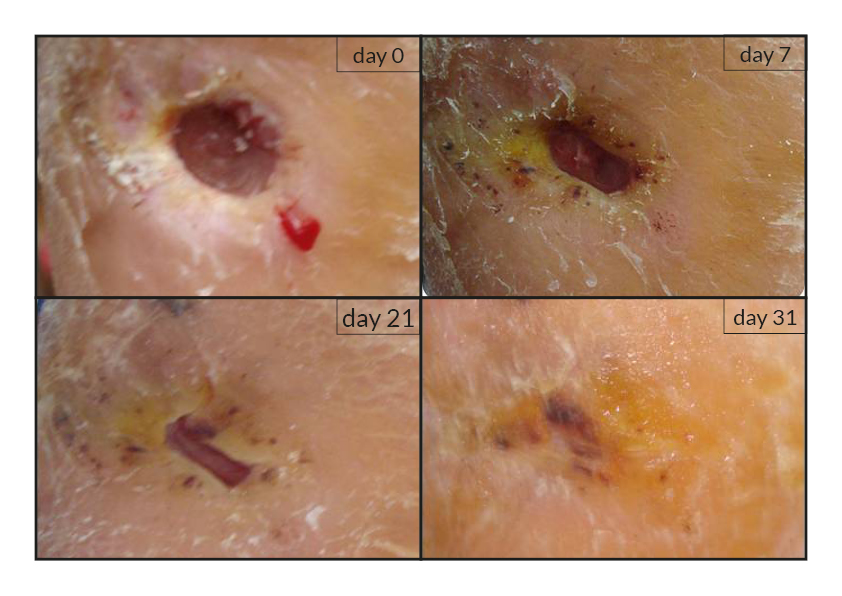
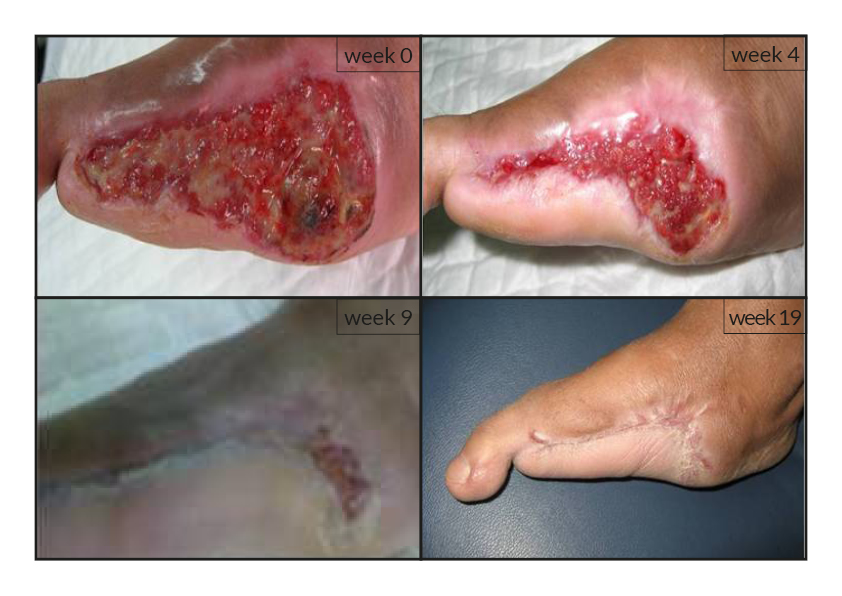
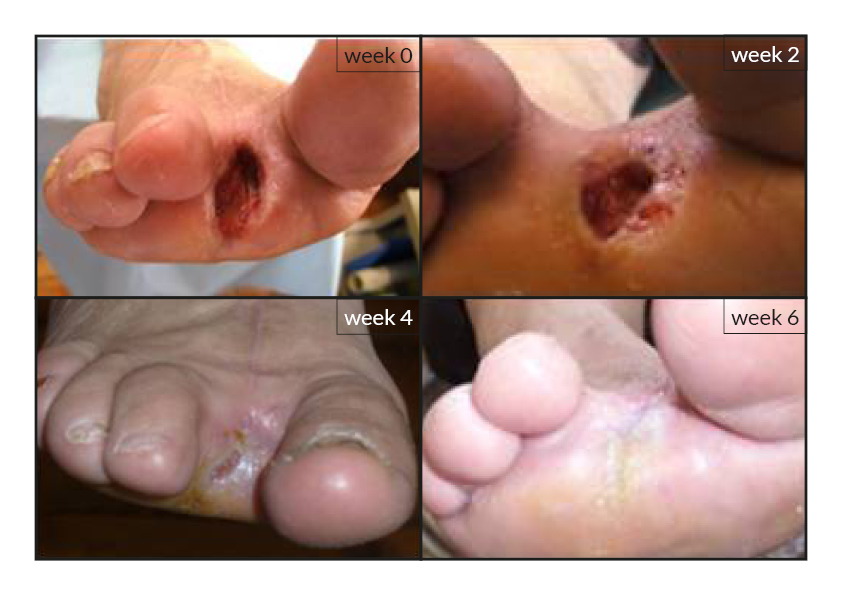
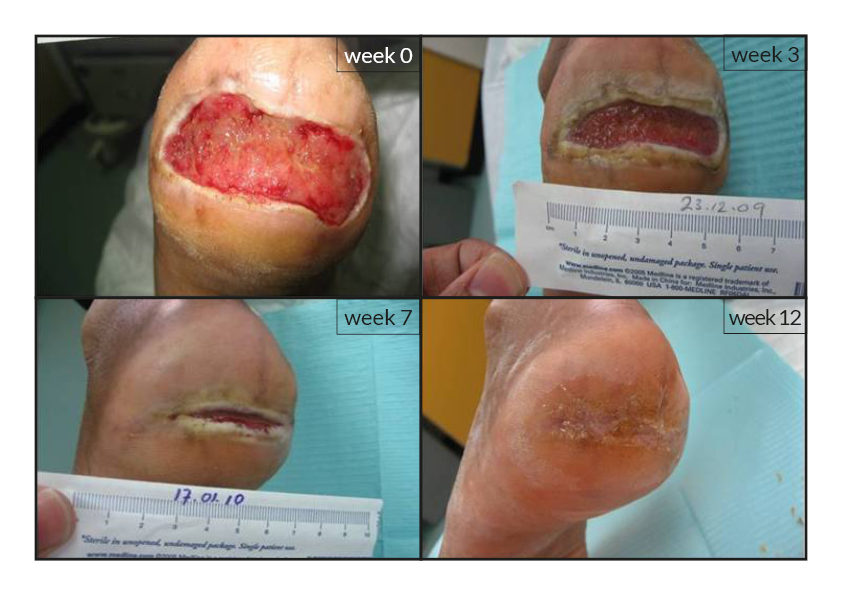
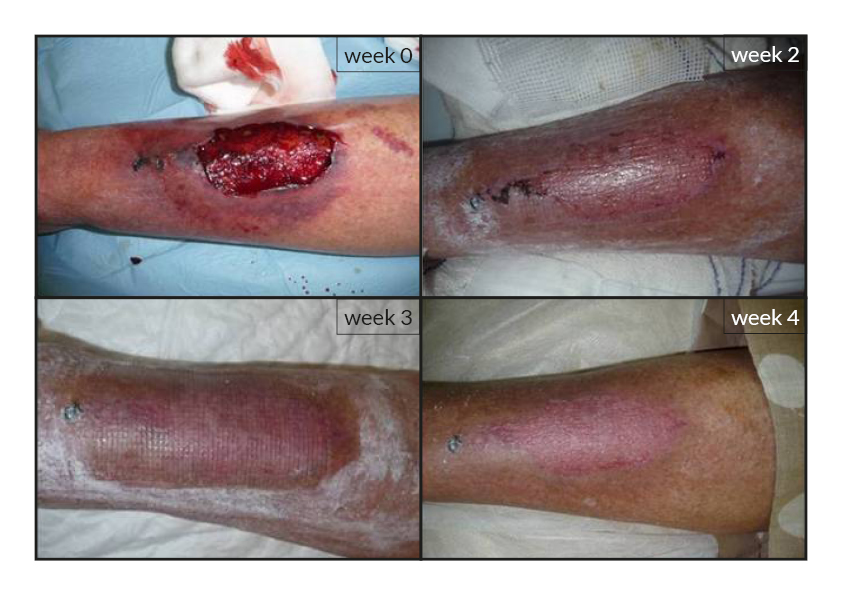
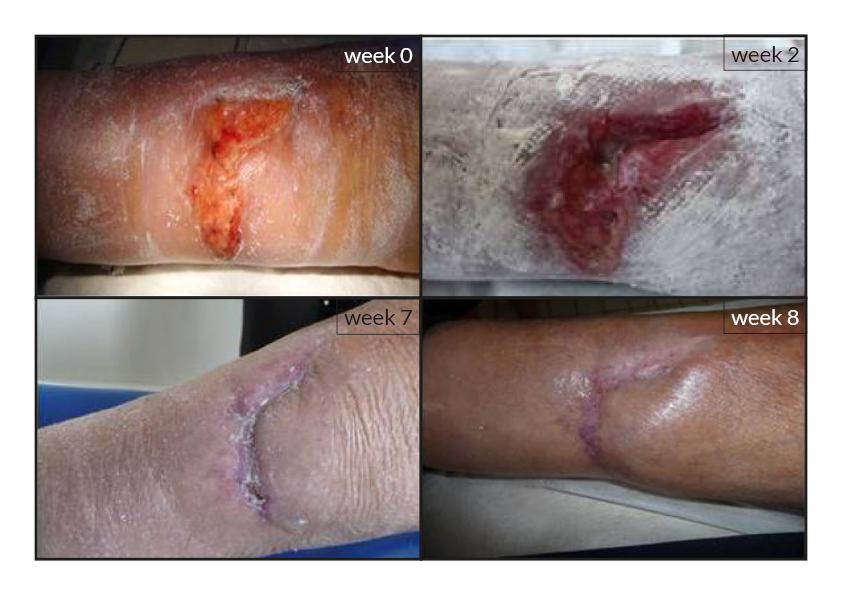
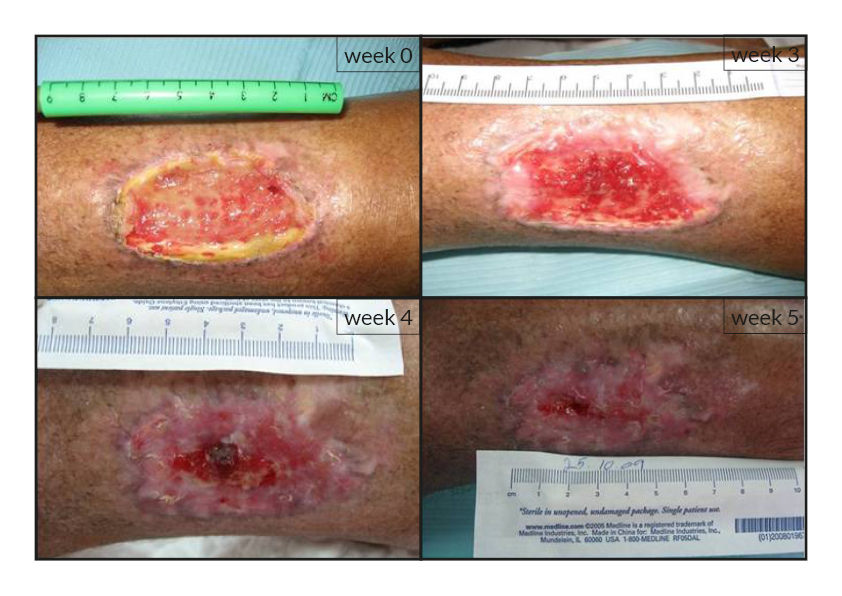
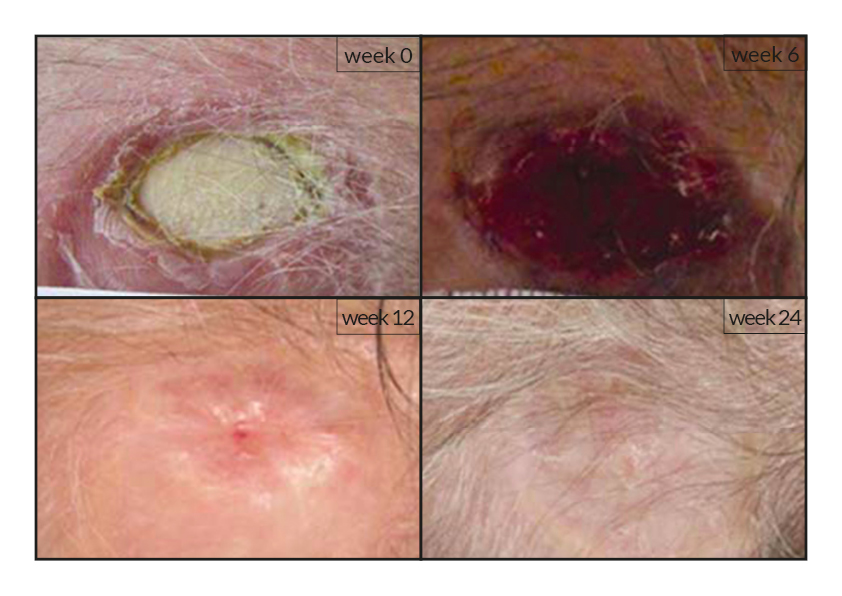
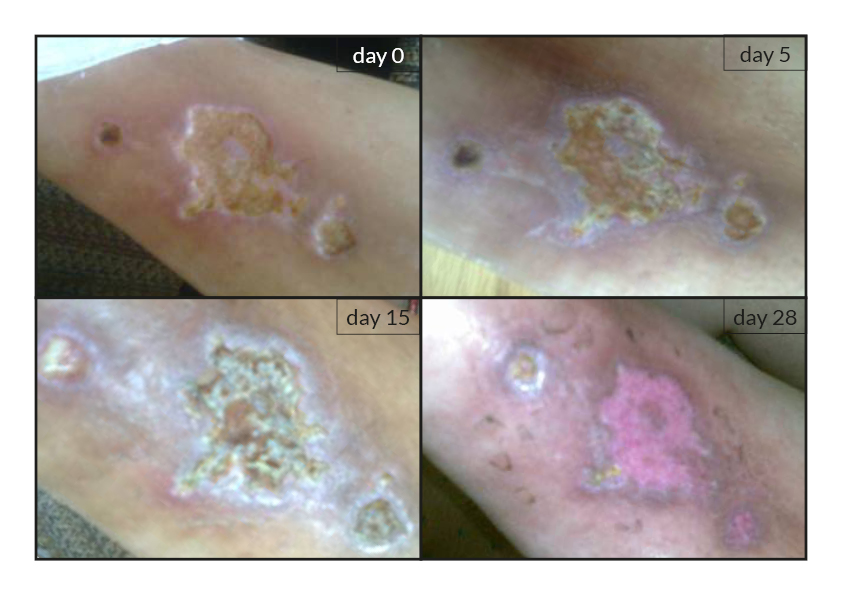
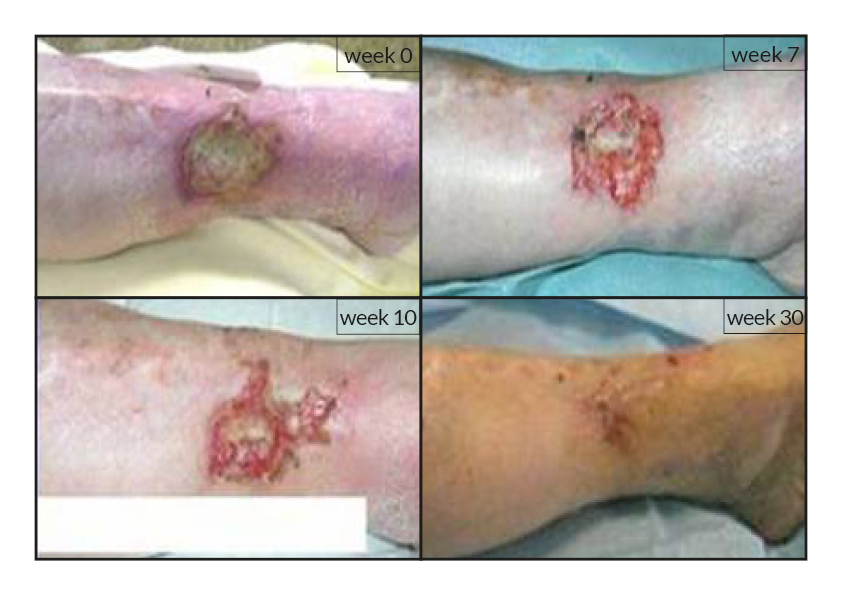
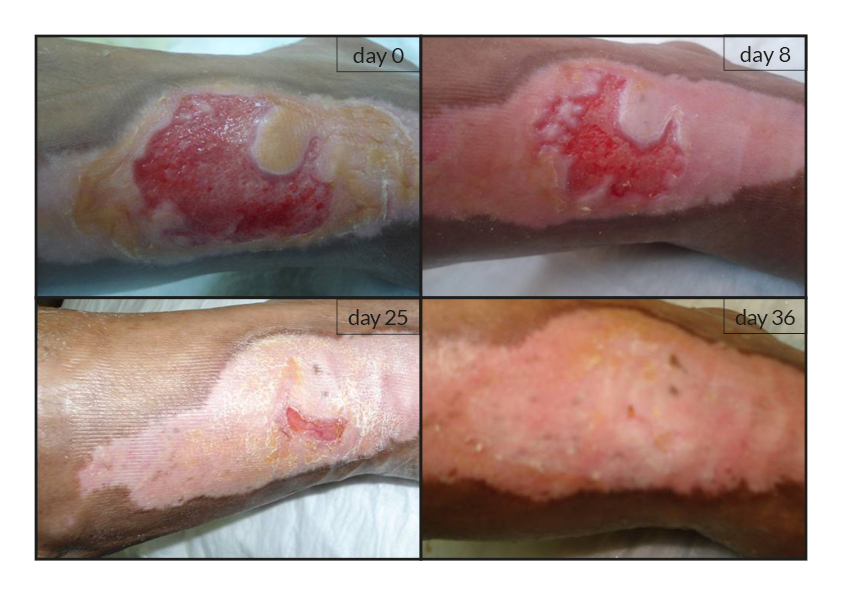
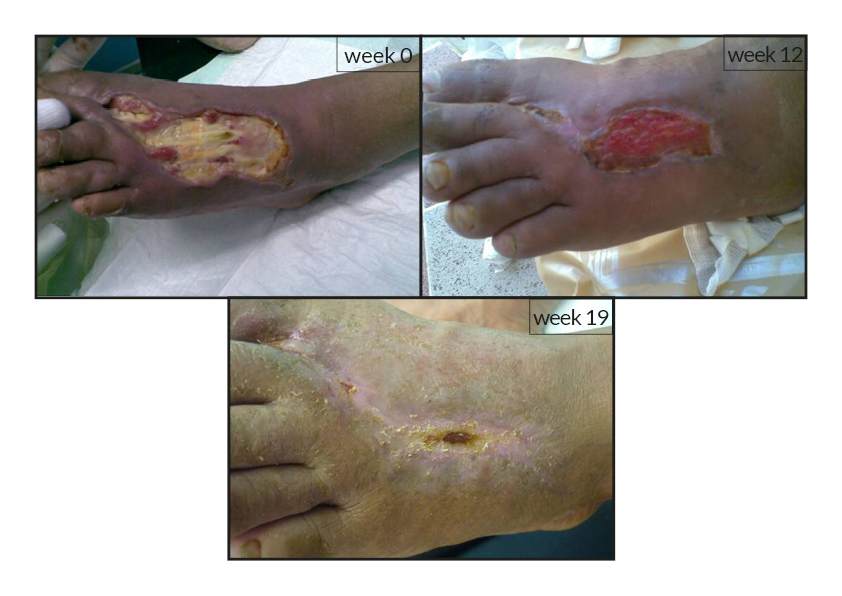
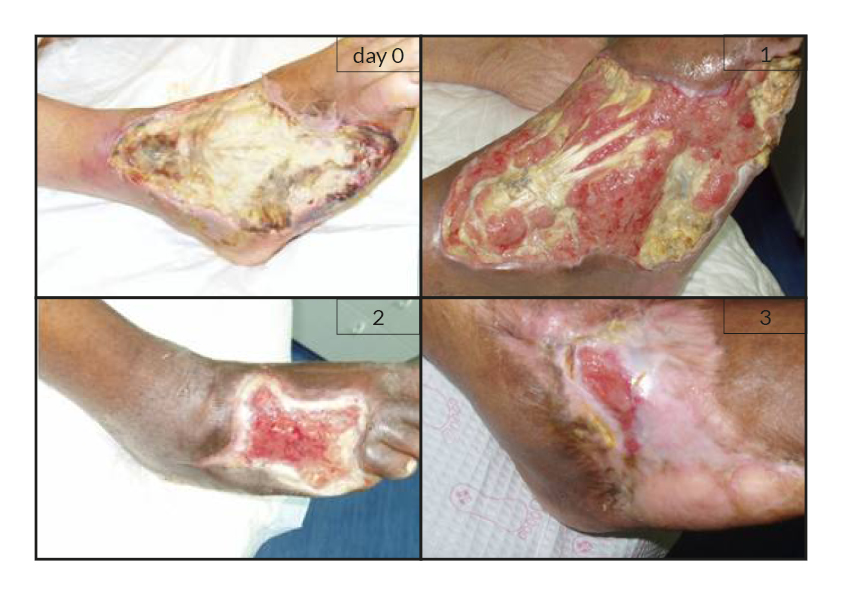
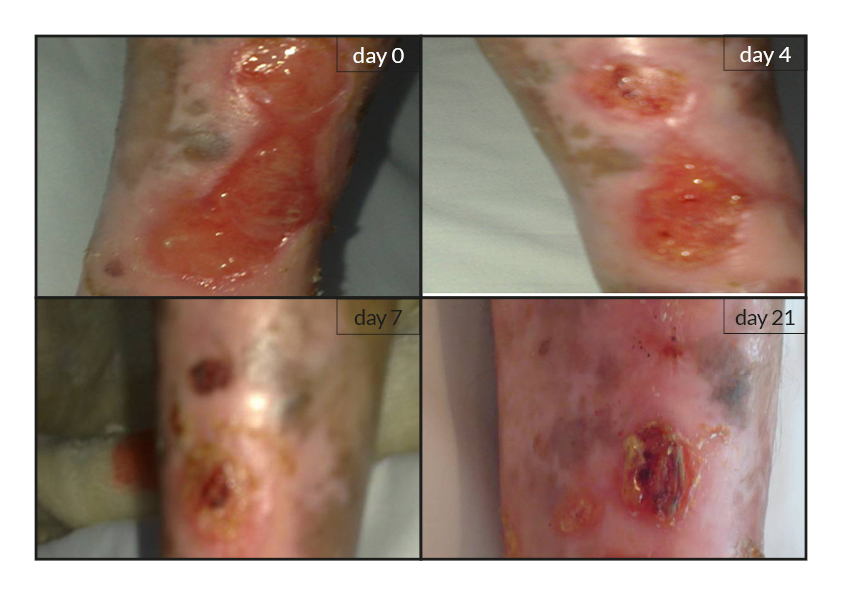
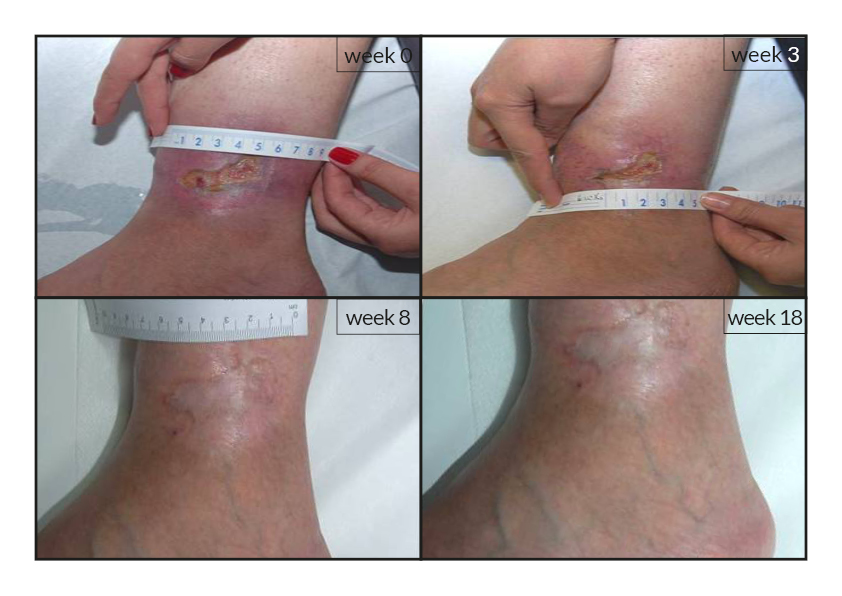
To date, tens of thousands of patients are benefiting or have been treated with the RGTA®-based therapy which was used to treat a wide range of wound types [1]. RGTA® abilities to heal skin wounds has been proven with patients mostly presenting with chronic ulcers associated with diabetes [2,3], limb ischemia [4], pressure ulcers, vascular-related cutaneous defects [5], burns [6] etc. which could be aggravated when patients undergo renal dialysis or immuno-suppression treatments (cases illustrated to the right). Moreover, RGTA® treatment successfully apply to patients presenting with ulcers caused by radiation [7] or some rare diseases such as epidermolysis bullosa [8], sickle-cell disease [9] or Stewart-Bluefarb syndrome [10]. In addition to chronic wounds, RGTA® were also used for treating acute lesions, such as after trauma or illustrated by cases of patients suffering from open wound trauma or recovering from reconstructive and plastic surgery [11].
Most patients treated with RGTA® are adults, but some successful results were observed with a 10-year-old patient presenting with Charcot’s syndrome, who ran a high risk of leg amputation.
Interestingly, pain relief was reported and measured in several cases by patients treated with RGTA® [4, 5, 8, 9]. Although, the molecular mechanism underlying this phenomenon is yet ill-defined, this observation is of great importance as to the role of RGTA® in injury treatment as well as patients’ quality of life.
Noteworthy, the patients treated with RGTA® have been presented with unsatisfactory treatment solutions as they failed to respond to standard treatment of wound healing and were considered in therapeutic failure. Altogether, these observations show the importance of RGTA® treatment with respect to the health state and the well-being of patients.
CACIPLIQ20® is the RGTA®-based product commercialized by OTR3. It increases the speed and quality of skin repair by protecting the matrix microenvironment of the wound.
1- Barritault, D., Gilbert-Sirieix, M., Rice, K.L., Siñeriz, F., Papy-Garcia, D., Baudouin, C., Desgranges, P., Zakine, G., Saffar, J.-L., and van Neck, J. (2016). RGTA® or ReGeneraTing Agents mimic heparan sulfate in regenerative medicine: from concept to curing patients. Glycoconjugate Journal. - PDF
2- Slim, I., Tajouri, H., Barritault, D., Njah, M.K, Ach, K., Chaieb, M.C., and Chaieb, L. (2012). Matrix protection therapy in diabetic foot ulcers: pilot study of CACIPLIQ20®. J. Wound Technol. 17 (V), 36–40. - PDF
3- Papanas, N., Demetzos, C., Pippa, N., Maltezos, E., and Tentolouris, N. (2016). Efficacy of a New Heparan Sulfate Mimetic Dressing in the Healing of Foot and Lower Extremity Ulcerations in Type 2 Diabetes: A Case Series. Int J Low Extrem Wounds 15, 63–67. - PDF
4- Desgranges, P., Louissaint, T., and Allaire, E. (2011). First clinical pilot study on critical ischemic leg ulcers with matrix therapy ReGeneraTing agent (RGTA®) technology. J. Wound Technol. 13, 44–8. - PDF
5- Groah, S.L., Libin, A., Spungen, M., Nguyen, K.-L., Woods, E., Nabili, M., Ramella-Roman, J., and Barritault, D. (2011). Regenerating matrix-based therapy for chronic wound healing: a prospective within-subject pilot study. International Wound Journal 8, 85–95. - PDF
6- Barritault, D., Al Harbi, S., Filipe, G.S. (2012) La thérapie matricielle une nouvelle branche de la médecine régénérative et ses applications dans le traitement des brulés: Du fondamental à la clinique. Brulure. 13, 23–7. - PDF
7- Neck, J.W.V., Zuidema, Y.S., Smulders, M., and Balmus, K.J. (20115-6). Unexpected healing of radiation-induced scalp lesions with OTR4120, a heparan sulfate mimetic. European Journal of Dermatology 451–452. - PDF
8- Malaq, A.A., and Denis, B. (2012). A Rapid Response to Matrix Therapy With RGTA in Severe Epidermolysis Bullosa. Eplasty 12, ic15. - PDF
9- Hayek, S., Dibo, S., Baroud, J., Ibrahim, A., and Barritault, D. (2016). Refractory sickle cell leg ulcer: is heparan sulphate a new hope?: Refractory sickle cell leg ulcer: is heparan sulphate a new hope? International Wound Journal 13, 35–38. - PDF
10- Hayek, S., Atiyeh, B., Zgheib, E. (2016) Stewart-Bluefarb syndrome: review of the literature and case report of chronic ulcer treatment with heparan sulphate (Cacipliq20®). Int. Wound J. 12(2), 169–72. - PDF
11- Zakine, G., and Le Louarn, C. (2010). Premières applications de la thérapie matricielle en chirurgie plastique et esthétique. Annales de Chirurgie Plastique Esthétique 55, 421–428. - PDF